Archetype Options
The Archetype Options Pricer allows the user to price and analyze the greeks of three products: European, American and Digital Options (Calls and Puts).
European Options
European Options and the behavior of their Greeks accept already been largely discussed in chapter four and chapter 5 respectively.
The Classic Options Pricer offers a perfect opportunity to put all this theory into practice.
American Options
American options can be exercised at any fourth dimension during their life. Since investors take the freedom to exercise their American options at whatever point during the life of the contract, they are logically more valuable than European options.
The Classic Options Pricer prices American Options using the approximation method of Bjerksund and Stensland (1993).
American Calls
For American Calls, early on exercise may be optimal just before the dividend payment if the dividend payment is big enough.
This tin be expressed past the following condition:
\(\frac{D}{Thousand} > r * (T-t)\).
Intuitively, if one exercises the American call, he pays a specific amount of money to purchase the underlying shares. On the 1 hand, he doesn’t receive interest on this greenbacks amount; and, on the other, he would receive future dividends for holding the stocks. In other words, if the dividend yield is college than the involvement rate until maturity, information technology is optimal to exercise the American call. For stocks not paying dividends, information technology is never optimal to exercise the American call.
American Puts
Ultimately, it tin can exist optimal for the holder of an American put option to cull to do if the interest rate that would be received on a cash eolith equal to Thousand is college than the dividend payments until maturity. For non-dividend-paying stocks, an American put should ever be exercised when it is sufficiently deep ITM.
It is important to realize that it makes no sense to exercice an option when in that location is time premium remaining because yous are throwing away that time premium by doing so. You lot would be better of selling the option than exercising it.
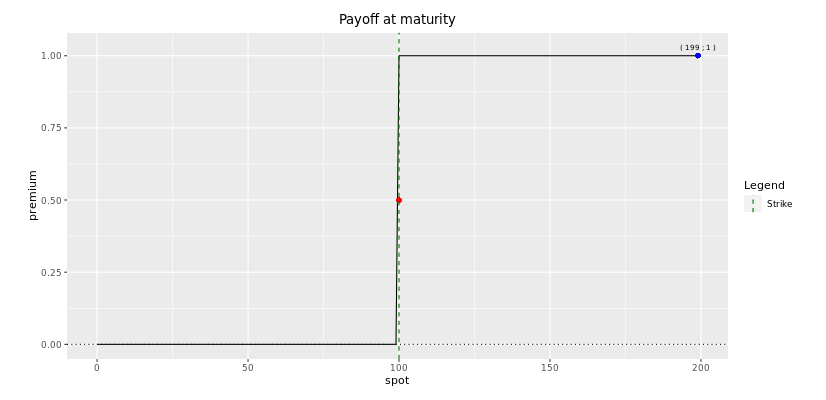
Digital Options
Digital options are quite straigthforward. They are options that pay a stock-still coupon if the underlying is beneath or higher up a predetermined level and does not requite a payout at all in all other cases.
Digitals are yet considered every bit exotic options equally they cannot exist perfectly replicated past a set of standard options.
European Digitals
We volition focus on Digital Calls but the aforementioned reasoning tin can always be applied in the case of Digital Puts.
Replication of European Digital Options
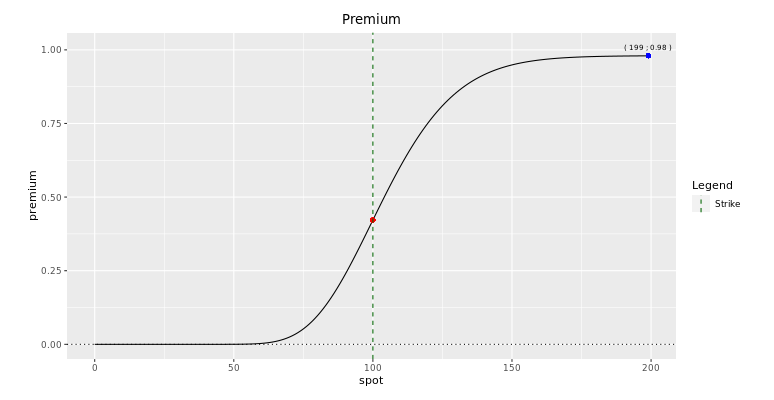
The digital call can be idea of as a limit of a call spread. One tin can therefore make a good estimate of the price of a digital option past using selection spreads.
Digital (K) =
\(\text{lim}_{\epsilon \rightarrow 0} \; \frac{1}{2 \epsilon} \left( Call(One thousand-\epsilon) – Phone call(K+\epsilon)\right) = – \frac{\partial Telephone call(K)}{\partial 1000}\)
Every bit the distance between the call option strikes and the digital strikes,
\(\epsilon\), gets smaller, we need
\(\frac{1}{\epsilon}\)
call spreads of width
\(2\epsilon\)
to replicate the digital. In the limit, meaning as
\(\epsilon\)
approaches zero, the telephone call spread replicates the digital exactly.
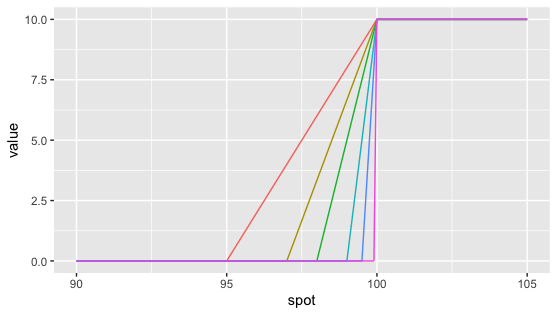
Notation that the above expression is theoretical as, in practice, a trader will non eye the call spread around the barrier. He will be more defensive and take a phone call spread that over-replicates the digital equally shown below.
Hedging a Digital
Well, you lot should not exist surprised if I tell yous that the only real manner to gamble manage the digital option is with option spreads.
Yous can then hedge a digital call equally a telephone call spread. The gearing of the call spread used to over-replicate the digital depends on the strike width of the call spread. The wider the call spread, the lesser the gearing and the more conservative the price.
What do we mean by proverb that the call spread over-replicates the digital option?
Let the states have a look at Fig 6.3. here above.
Above the barrier level, the call spread has the same payoff every bit the digital call. Below the barrier level, the digital call has a zero payoff but the call spread has a non-zero payoff between its lower strike and its upper strike located at the barrier level. Therefore, we say that the telephone call spread over-replicates the digital call because its payoff (and therefore its premium) is e’er greater or equal to the digital call’s payoff.
Let us take a small practical example.
As an investor, you buy a 6-calendar month European digitall call on AB Inbev which pays 10€ if after 6 months the ABI stock trades above fifty€ and pays 0 if the ABI stock trades below 50€ at maturity.
As a trader, I sell you this digital call on ABI stock. How much will I sell information technology to yous? Well, I will replicate the digital using a geared call spread. I believe that a two€ wide call spread should exist enough for me to risk manage this position. So I will toll the digital telephone call as if it was a 48€/50€ call spread that is v times geared.
Y’all can think of different scenarii and run into that this call spread over-replicates the digital call.
By doing so, I accept therefore priced the digital conservatively. I could have been more aggressive by choosing a tighter 49€/50€ call spread. But retrieve that I accept risks to manage, especially gamma and pin take chances around the 50€ barrier level.
The smaller the call spread, the more ambitious the price but the more difficult the hedging.
For a digital selection, Gamma can exist quite big and tricky about the bulwark at maturity. Think about the situation where you are just before expiry, the ABI stock trades at 50€ and so that the digital would not pay you anything. If ABI stock goes up to fifty.02, the digital would suddenly pay y’all x€. As a trader, this would be extremely hard to hedge. Equally a trader, the telephone call spread gives me a cushion against this hazard.
Using a call spread allows to shine the Greeks. The smaller the call spread, the larger Gamma and Vega can go near the bulwark. In fact, around the barrier level, they shoot up so shoot down while changing sign.
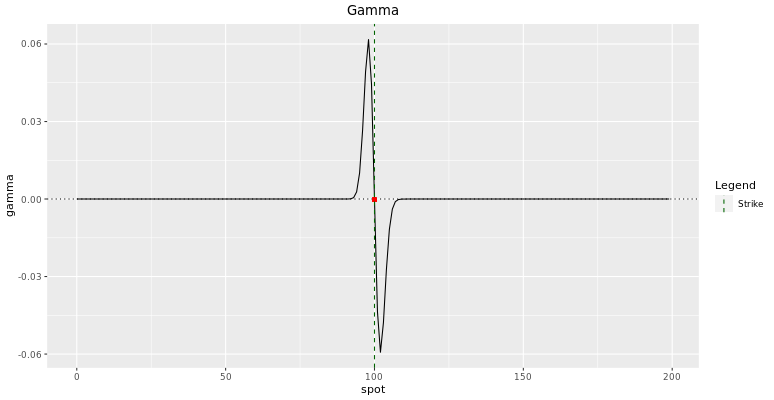
We will analyze Call Spreads in more details in the next chapter. You will see that its gamma is smoother than that of a digital telephone call. The larger the strike width, the more this is truthful.
You shoud accept understood past now that when I sell a digital phone call, I actually volume and merchandise a call spread in my risk management system. As the underlying gets closer to the barrier, you lot still want to be able to manage your delta hedge properly. A large Gamma means that you will accept to buy/sell a big Delta of the underlying, which might be hard in the market. It is the reason why the liquidity of the underlying is an of import variable when selecting the strike width of the replicating telephone call spread.
Width of the Call Spread and Barrier Shifts
And then the width of the pick spread is used equally a pricing mechanism to go conservative on the price of a digital option over its model price.
It is necessary in the pricing mechanism to account for real-world difficulty in executing large deltas at the barrier that the model does not consider.
The optimal width of the telephone call spread depends on several parameters among which the size of the digital, the size of the nominal, the underlying’s liquidity, the tiptop delta around the barrier and the implied volatility around the barrier.
In practise, some traders rather take a constant shift of the barrier. Basically, it allows them to take an additional margin for managing the risks if the underlying was to get close to the barrier. This can be more efficient when hazard managing a big book of exotic options.
When taking a bulwark shift, a trader is pricing a new digital whose replicating
centered
phone call spread is the hedge of the actual digital.
The management of the bulwark shift apparently depends on the trader’s position.
We volition discuss farther about barrier shifts in the chapter on barrier options.
Run a risk Analysis – The Greeks
We will shortly speak about the greeks of a digital call at initiation. Note that the risks and therefore the greeks are dynamics. For example, the greeks volition be quite different if you get closer to maturity. As I cannot depict every scenario, the best mode for you to learn this material is to use the pricer, ask yourself many questions and notice your answer using the pricer. For example, what happens to the greeks if just before maturity the spot price is exactly at the bulwark level? Yous open the pricer, yous select Digital call in the selection type input, you gear up the stock price at the strike level and yous prepare the maturity close to 0. You will be able to calculate the greeks and run into all the related graphics. You lot will and then take to interpret them. If you have any questions, you can ever drop the states an email at info$@$derivativesacademy.com
Delta
The holder of a digital call is always long the forwards toll since a higher forward increases the probability of the option finishing in-the-money.
Beingness long the frontwards means being: – Long involvement rate – Short dividends – Short borrow costs

Fig: vii.v :Delta of a ane-year Digital Call at initiation
I don’t think I am making you a favor if I describe all the graphics with precision. The all-time way to develop yourself is to decipher these plots by yourself. For example, yous should be able to understand why does the delta converges to zero (and non to ane as in the case of European calls) when the stock toll increases well above the barrier level. Note that the plot of the delta is just the beginning derivative of the premium plot with respect to the spot toll.
Since a digital call has positive delta, the trader selling information technology will have to buy delta of the underlying. Therefore the trader will be long dividends, short interest rates and long borrow costs of the underlying.
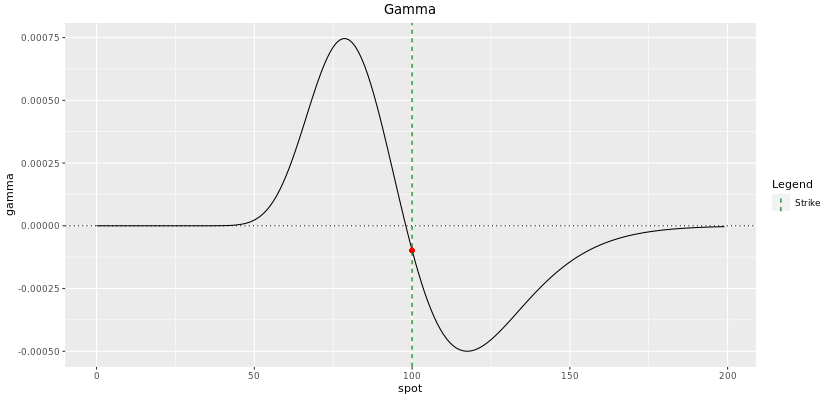
Gamma
While their magnitudes are quite unlike, Gamma and Vega behave similarly and depend about the position of the forwards toll regarding the barrier. The Gamma plot tin can be easily deduced from the Delta plot since it is merely the first derivative with respect to the spot toll. Different vanilla options, the gamma of digital options change sign effectually the barrier level. While this change is quite smooth at initiation, we take seen that information technology gets more than spiky closer to maturity. Information technology makes the hedging procedure particularly hard for the trader as vega and gamma shoot up and down while changing sign.
Think about being the trader hedging this digital call close to maturity when the spot is around the barrier level. How does this modify of sign impact your delta hedging?
This discontinuity risk (gap chance) has been discussed and is the reason why bulwark shifts are applied and option spreads are used to smooth it.
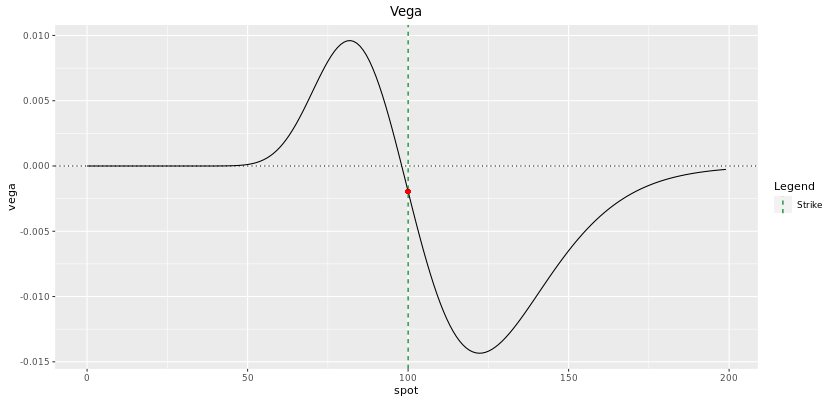
Vega
The fact that vega depends on the position of the forrard price with respect to the barrier is very intuitive.
The holder of a digital phone call volition be long volatility if the forward price is lower than the barrier level since a higher volatility will increase the probability of the spot finishing above the barrier at maturity. When the forwards is lower than the bulwark, you can think of the digital phone call equally being out-of-the money. Volatility will increment the probability of the option going from OTM to ITM.
Inversely, the holder of a digital call will be brusque volatility if the forrad price is greater than the bulwark level since a higher volatility volition decrease the probability of the spot finishing to a higher place the barrier at maturity. When the forwards is greater than the bulwark, yous tin can recollect of the digital call every bit being in-the coin. Volatility volition increase the probability of the option going from ITM to OTM.
Theta
The shape of Theta plot looks completely opposite to the shape of Vega plot. This is because time to maturity has a similar issue to a digital option price as volatility. The effect is not exactly the aforementioned equally time has always a second effect that comes from the discounting impact, altough this last effect is generally less of import.
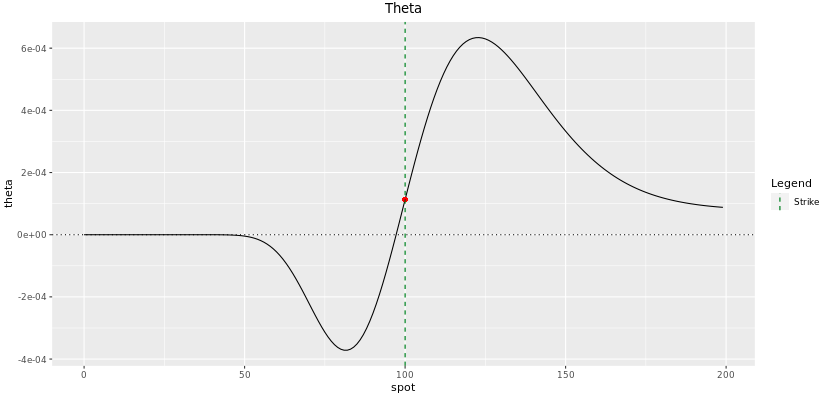
Fig: seven.8 : Theta of a one-year Digital Call at initiation
Rho
When we spoke about Rho in section five.6.one, we said that the result of involvement rate on an option’s toll came from two effects: the cost of delta-hedging and the discounting.
It is therefore not very surprising to see similarities betwixt the Delta profile and the Rho profile. Annotation that the discounting issue is clearly apparent in the right-side of the bend where the option is completely in-the-coin and in that location is no delta left. On that side of the curve, Rho is negative because an increase in interest rates inscreases the discount gene and therefore decreases the present value of the digital call. How much the Rho is negative will then mainly depend on the time to maturity.
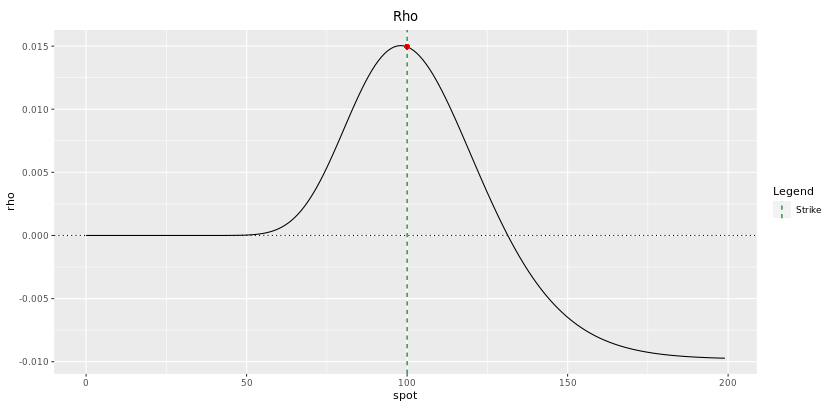
Fig: 7.nine : Rho of a one-yr Digital Call at initiation
Skew
Since a trader hedges a digital option using an option spread, the skew adventure is a critical consideration.
Allow usa assume that we merely sold a digital call, we will hedge it past ownership a call spread. Taking a long position in a telephone call spread means buying a call at a lower strike and selling a call at an upper strike. The skew makes the lower strike implied volatility more expensive than the upper strike unsaid volatility. Since the skew makes the hedge more expensive, it makes the construction itself more expensive. Remember what nosotros said in section 4.v, an option cost is aught else but the cost of the hedge!
Therefore the skew makes the price of digitals more expensive. – A long position in a digital call is long the skew. – A brusk position in a digital telephone call is short the skew.
Since digital options are sensitive to skew, you lot must utilise a model that knows nigh skew. When pricing European digitals, then your calibration should focus on getting the skew at maturity correct. When pricing American digitals with path-dependency, you will need to utilise some smooth surface calibration to capture the outcome of surface through fourth dimension. In other words, when dealing with these path-dependent american digitals, you are not only sensitive to the volatility at maturity but to many volatilities earlier maturity. Your volatility hedge will then consist of several European options with different maturities. We speak about vega buckets. The book of Adil Reghai is particularly good to grasp the concept of vega buckets and vega KT.
American Digitals
For American digitals, the trigger condition tin be activated at anytime before maturity.
At that place exists a fantastic approximate link between European digital options and American digital options.
I felt quite stupid while learning well-nigh it as it is actually quite intuitive :). Back in 2015, I used to try estimating the price of every exotic option before pricing them. I was trying to develop as much as possible my intuition in terms of pricing and sensitivities in every market scenario. I rapidly realised that the price of American digitals were always approximately twice the toll of European digitals (with the same characteristics obviously!). The price of European digitals beingness quite like shooting fish in a barrel to approximate, the approximations for American digitals were not as well bad. Ane 24-hour interval, I decided to stay a scrap later on the flooring and start plotting Monte Carlo simulations to compare the toll sensitivity of a barrier pick to the barrier level with respect to the underlying’s frontwards. Doing and then, I realised why the in a higher place relationship between American and European digitals were then consistent. This is simply the consequence of a well-known principle followed by brownian motion: the reflection principle.
The Reflection Principle
In the theory of probability for stochastic processes, the reflection principle for a Wiener process states that if the path of a Wiener process W(t) reaches a value Westward(s) = a at fourth dimension t = s, then the subsequent path afterward time s has the same distribution as the reflection of the subsequent path about the value a In other words, if W(due south) = a then W(t) is just as likely to be above the level a as to be beneath the level a for s < t.
By assuming in our models that the log-returns of the underlying are unremarkably distributed with cypher log-migrate (with mean zippo), the normal distribution introduces the symmetry of the reflection principle.
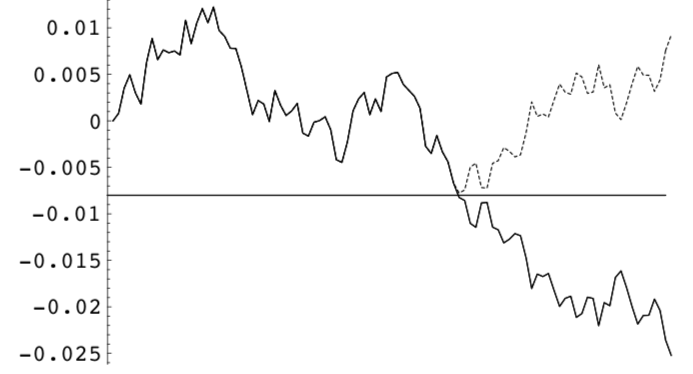
Gatheral expresses information technology nicely in his lecture on Barrier options. In Fig 6.5 below, the dashed path has the same probability of being realized as the original solid path. We deduce that the probability of striking the barrier B is twice the probability of catastrophe up below the barrier at expiration. Putting this some other fashion, the value of an American digital option is twice the value of a European digital pick. Note that this relationship won’t be exactly respected when the log-migrate is non zero (understand when the forward level is unlike from the spot level).
No-Impact Options
No-touch digital options pays a coupon if the barrier has never been touched during the option life.
It seems clear that the event of never touching the bulwark is complementary to the effect of ever touching information technology. Therefore, the probability of never touching the barrier is nothing else simply 1 minus the probability of ever touching the barrier. From this parity, we can easily deduce the price of a no-bear upon digital option knowing the price of the american digital option and vice versa.
Source: https://bookdown.org/maxime_debellefroid/MyBook/classic-options.html